Javascript ES6
Variable declaration
Array Helpers
For Each
Map Helper
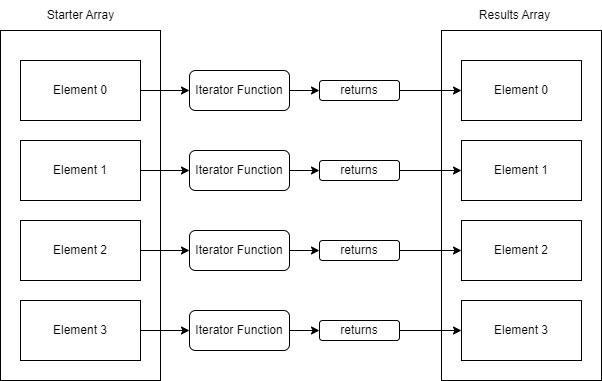
Filter Helper

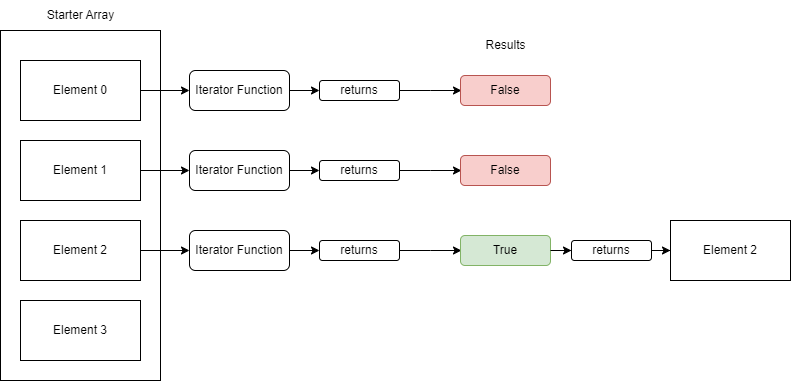
Find Helper
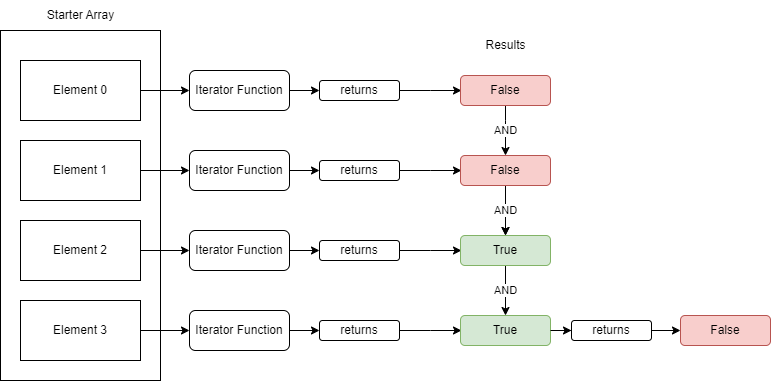
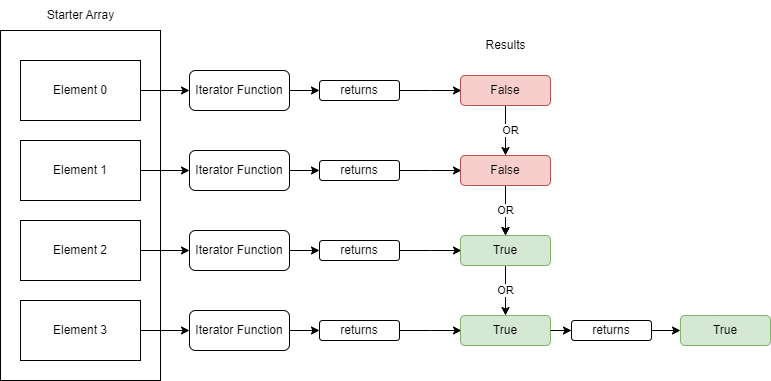
Every and Some Helper
Reduce Helper
Rest and Spread Helper
Destructuring
Classes
Last updated